A detailed understanding of diamond symmetry
Posted by Hari Krishna
November 30, 2022
Telling one diamond apart from the other is not easy, especially because they look identical and at the most, it is usually a grading report that can reveal the differences. Symmetry is something that is taken into consideration while determining the quality and value of a diamond and reflects in a grading report.
Diamond Symmetry is one of the important elements to look at in a diamond. But how can we know the symmetry in a diamond? Can one see it? Unlike cut, color, or clarity, it’s difficult to tell the difference between a diamond with a “good” symmetry rating and one with an “excellent” symmetry rating.
Before we get into the details, we need to understand what exactly this concept means.
Symmetry in a diamond is a combination of different aspects of its structure. It is how the diamond comes together and forms a shape which actually depends on precision of the cutting and overall craftsmanship.
Let’s understand the individual aspects to fully understand diamond symmetry.
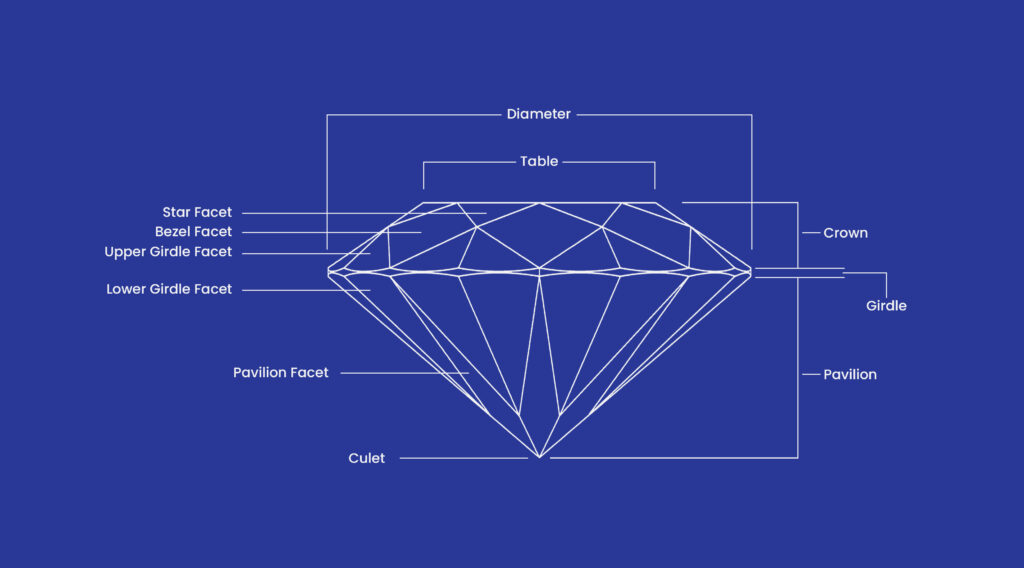
The precision with which a diamond’s facets align and intersect is referred to as symmetry. It is defined by how symmetrical the facets and angles of a diamond are. Is the table’s culet centered? Is the size and shape of all the facets uniform? Based on these things, the grade of symmetry is determined by a gemologist.
Extra or misshapen facets, off-center culets and tables, and wavy girdles can all be examples of asymmetrical diamonds which can also be known as symmetry defects.
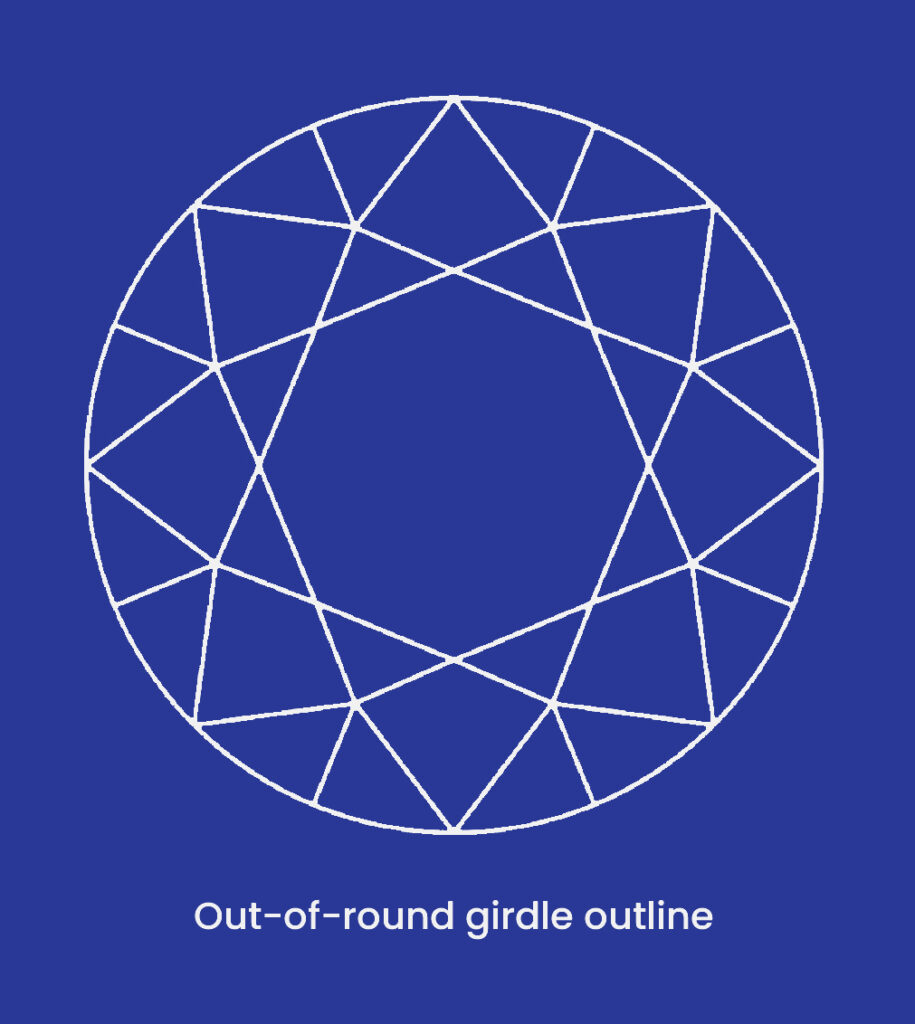
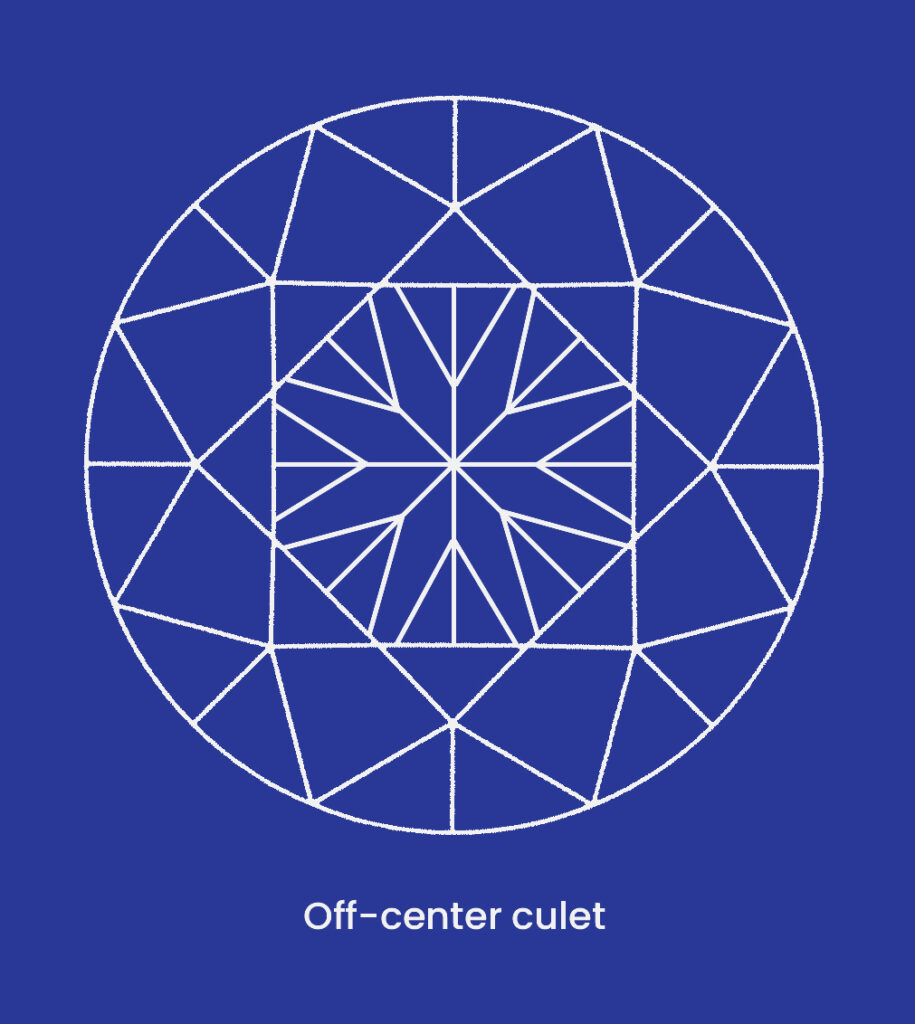
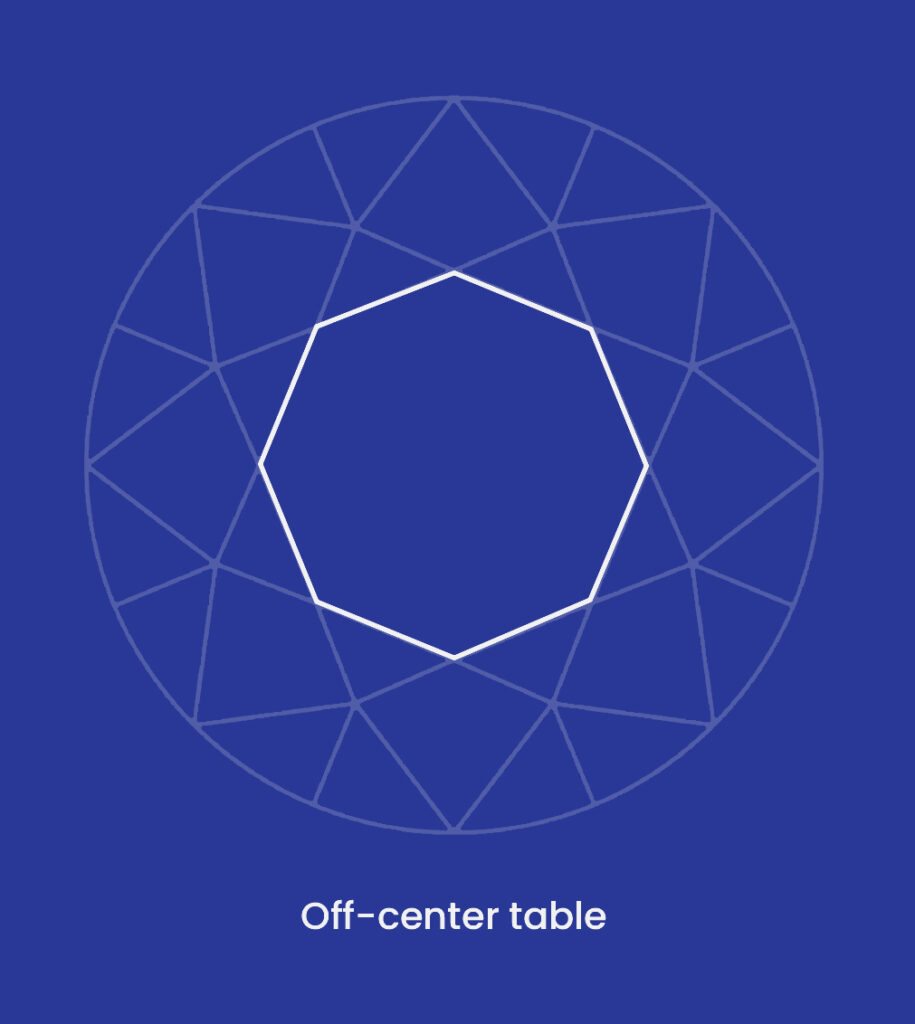


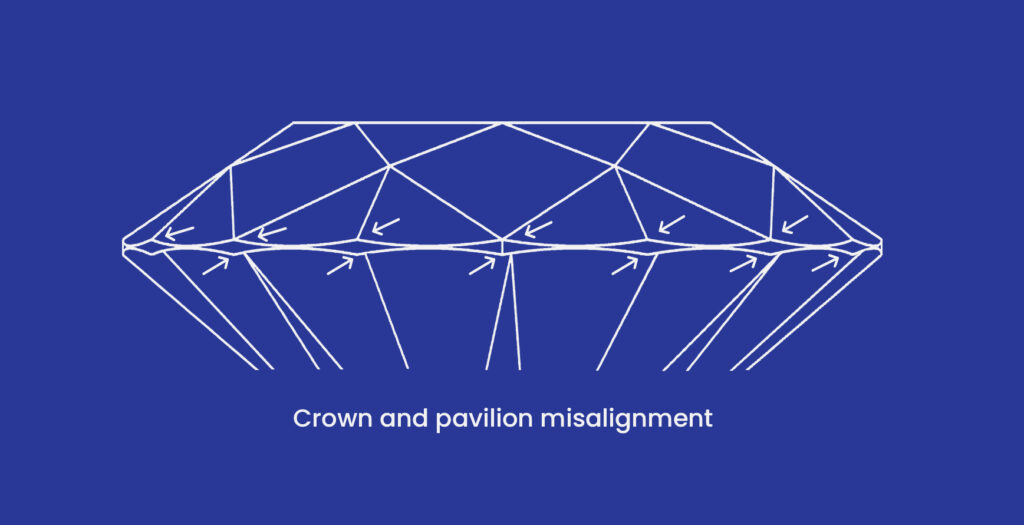
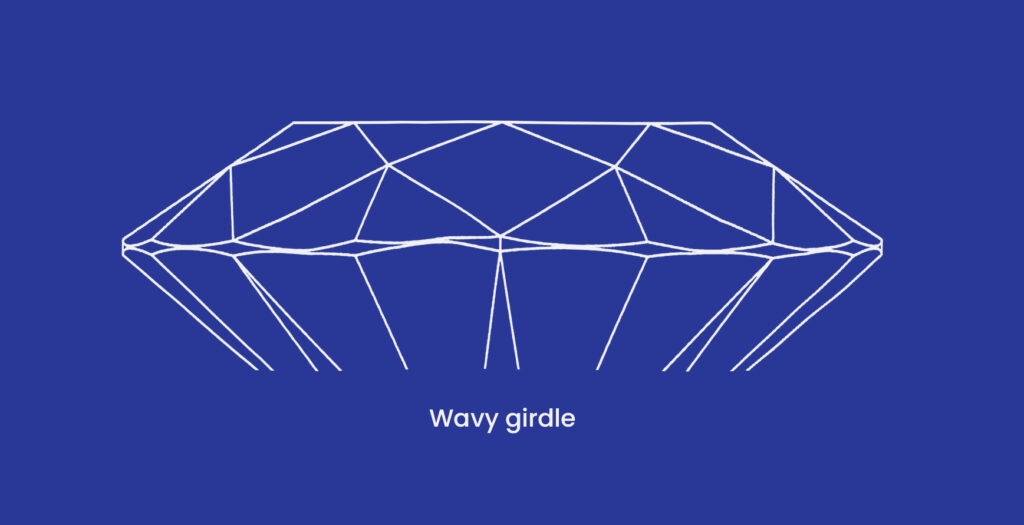
The GIA assigns symmetry grades of Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, and Poor. The visibility and presence of deviations at 10x magnification are used to determine the symmetry grade.
Let’s learn about some of the factors of the diamonds’ symmetry grading, defined by GIA.
• Excellent: Excellent symmetry means that there are very few deviations in a diamond. Their tables are perfectly centered, with no extra or missing facets.
• Very Good:Very Good symmetry diamonds have a couple of minor flaws. A slight misalignment or a misshapen facet could be present.

• Good: Diamonds with good symmetry have a few deviations. A pavilion angle variation or a missing facet could have an impact on the diamond’s brilliance.

• Fair: Diamonds with fair symmetry have several deviations. Misalignments, variations, and misshapen features reduce the diamond’s brilliance.
• Poor: Diamonds with a Poor symmetry grade have several noticeable flaws. The diamond will most likely appear dull. An off-center table, missing facets, variations, and misshapen facets could all be present.
Symmetry of a diamond is determined by its cut quality. The criteria outlined in the AGS and GIA grading systems are a fantastic resource when looking for a stone that meets your needs.
The value of a diamond is affected by every aspect or characteristic that is used in the grading process. Diamonds with “Fair” or “Poor” symmetry are generally considered to be less valuable.
Symmetry depends on the expertise of the craftsmen who plan, cut and polish a diamond. So if you are looking for the best and most symmetrical diamonds, choose the right diamond manufacturer.
Hari Krishna Exports is among the top 10 diamond companies of India and largest exporters of GIA certified loose diamonds, ranging from 0.18 cent to 50+ carats-sized diamonds in more than 9 shapes, including brilliant-round cut, FL to I3 clarity, and D to M Color across the 80+ countries of the world, including the USA, Hong Kong, China, Australia, Israel, the UK, Canada, etc.
Sign up here to receive the latest updates on diamond jewelry, industry trends or if you are interested in knowing about how we maintain sustainable practices being in the natural diamond industry.